
The dynamical action of the gratings is discussed, and the anomalous behavior is shown to be due to the presence of exceedingly narrow diffracting elements, which may be present even in the case of rather coarse rulings. The spectra formed by the Al grating are completely plane polarized, because of the circumstance that the width of the scratches is considerably less than the wave-length of the light.


2.7 Diffraction Efficiency 2.7.1 Definition The grating equation. This obtains, however, only when the grating space is equal to an integral multiple of λ (for normal incidence) which means that the dark bands correspond to λ values which are passing off the grating on both sides at grazing emergence. Another application of gratings in waveguides and fibers is to mutually couple two ( or. The dark bands appear to be due to the circumstance that diffracted wavelets from the lines are inhibited by the collective effects from neighboring lines, i.e., there is a sort of destructive interference along the plane of the grating. The behavior of the bands as the incidence angle is altered has been very completely recorded by photography and the energy missing in the grating spectra has been found in excess in the spectrum of the central image. A diffraction grating is made by making many parallel scratches on the surface of a flat piece of some transparent material. Our gratings are the principal component in a spectroscope and are used for experiments. The quality of the spectrum produced from our gratings is the brightest possible with a minimum of distracting visual noise. The present work was done with a chromium plated echelette grating of 7200 lines to the inch ruled on copper, and one of 15,000 lines ruled by Dr. Diffraction Gratings are used for the direct viewing and analysis of spectra from different gas tubes and other light sources. They provide the critical function of selecting the wavelengths of light required to. The grating acts as the dispersive element at the heart of many modern spectroscopic instruments. Classical theory has never accounted for these anomalies, though tentative efforts were made at the time by Lord Rayleigh. Diffraction gratings are optical components with a periodic structure that separate light into beams traveling in predictable directions based on their wavelength. They show narrow bright and dark bands in the continuous spectrum of a white source.

Paul Walorski, B.A.Gratings similar to those described and studied by the author in 19 have been more fully investigated. It is the same advantage of using a reflecting telescope over a refracting one. The switching time of the microfluidic diffraction grating is, however, longer than that of a reconfigurable diffraction grating 0.5 ms that. The advantage of a grating over a prism is that light passing through a prism can be absorbed (and lost), while a grating's reflected light spectrum does not have to be transmitted through any material. diffraction gratings: a sensor based on a periodic array of colloidal crystals in a hydrogel 2 had an equilibrationwx time of 30 s a grating based on liquid crystals 1 had awx switching time of 20 ms. You can see this color separation by looking at white light reflected from the grooves of a CD.
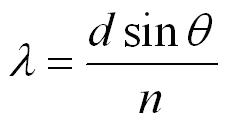
We mostly make gratings with nanoscale periods (often referred to as pitches) for x-ray. A light ray reflected (or transmitted) by a grooves in the grating will either interfere constructively or destructively with the ray from the groove next to it, depending on the angle it emerges and the light's wavelength. Izentis LLC designs and builds a variety of diffraction gratings. To allow that analysis, the star's total emitted light must be broken down into individual wavelengths just at a prism or rainbow separates sunlight into distinct wavelengths, or colors.Ī prism takes advantage of dispersion, which results from the fact that different colors of light travel through glass at different speeds, depending on wavelength.Ī diffraction grating can accomplish the same separation of colors because of diffraction. Information about a star's composition, magnetic fields, motion, temperature and pressure can, therefore, be obtained by analyzing its light's intensity at each wavelength. This is because: the light passing through each slit is diffracted. Each element has a unique 'fingerprint' determined by the allowable electron energies surrounding its nucleus, causing it to emit or absorb specific wavelengths of light. at a diffraction grating, light is transmitted by the grating in certain directions only. How do diffraction gratings tell us information about distant stars and galaxies?Īnswer The connection between diffraction gratings and stars is found in spectroscopy, which is the study of the relative brightness of an object at each wavelength of light (electromagnetic radiation) it emits or absorbs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
